The UX Process – What is Involved?

The UX process is an approach for designing products or services that fit into users lives rather than forcing users to change their behavior to adopt a new product or service.
The 3 key phases of the UX process are discovery, design and feedback:
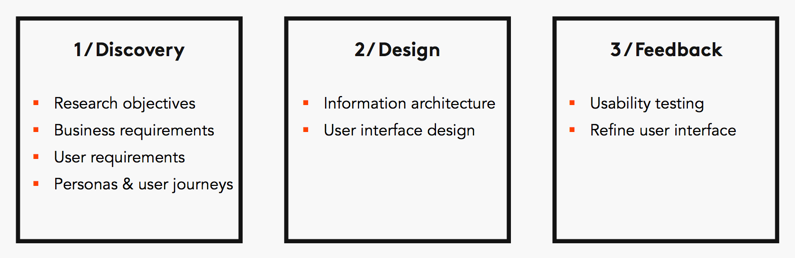
First, we will conduct a discovery phase to gather business and user requirements. To understand what the business wants to achieve and what the users’ needs and expects from the business.
We will then move to the design phase where we create the information architecture and user interface designs based on the user and business requirements. The information architecture (IA) focuses on organising, structuring, and labelling content in an effective way. The goal is to help users find information and complete tasks. The user interface design is focused in what users will see on each screen or page (navigation, information and interactive elements) to accomplish a specific purpose.
During the feedback phase, we put the design in front of users and test whether it meets their expectations and needs and refine the design based on their feedback.
It’s important to note that the UX process is often not linear, instead, it might include several iterations. For example, after implementing some changes in our designs we might conduct another round of usability testing to confirm the new version of the design meets the user needs.
The discovery phase is one of the most important parts in the UX process because it helps understand your audiences before you start designing for them and helps identify the problem before trying to solve it. This forms the foundation of a good product and services.
The structure of the discovery phase varies across each project and it is tailored and directed by what you want to achieve through the research. Usually, there are three areas of focus and they are:
- Business research The aim is to understand what you want to achieve, what are the areas of focus, and how success ought to be measured. The research needs to align with the overarching business strategy.
- User research User research focuses on understanding user behaviours, needs, and motivations. There are a plenty of research methods, including interview, workshop, and context enquiry and diary studies.
- Heuristic evaluation We can conduct a heuristic evaluation on an existing product, to understand its strengths and weaknesses and identify key areas of improvement for the re-design process.